SVX Power Steering Systems on Early Subarus Part 4:
There are two model-specific systems available on SVX vehicles:

• The engine speed sensitive, or conventional belt driven hydraulic pump and pinion type steering system is standard equipment on the SVX.
• An SVX equipped with the SVX Touring Package uses an optional vehicle speed-sensitive system. This system provides normal power assist at low vehicle speeds for reduced driver steering effort, and reduced steering assist at increased vehicle speeds for increased road feel and improved engine operating efficiency. Both systems have many similarities with the Legacy system.
SVX Power Steering Pump
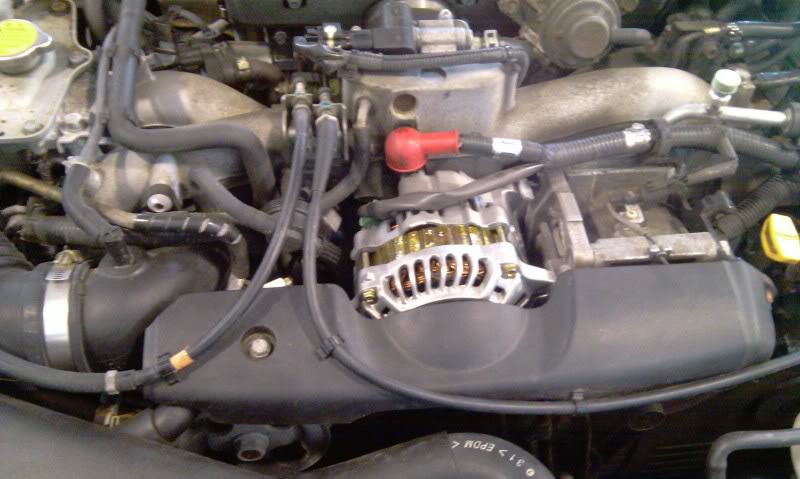
Both systems share many similarities to existing Subaru steering systems. Both use a belt driven power steering pump, although the pump housings are different in appearance.
Rack
A conventional power assisted rack with the standard Subaru lines and hoses is used by the standard system.
Oil Cooler
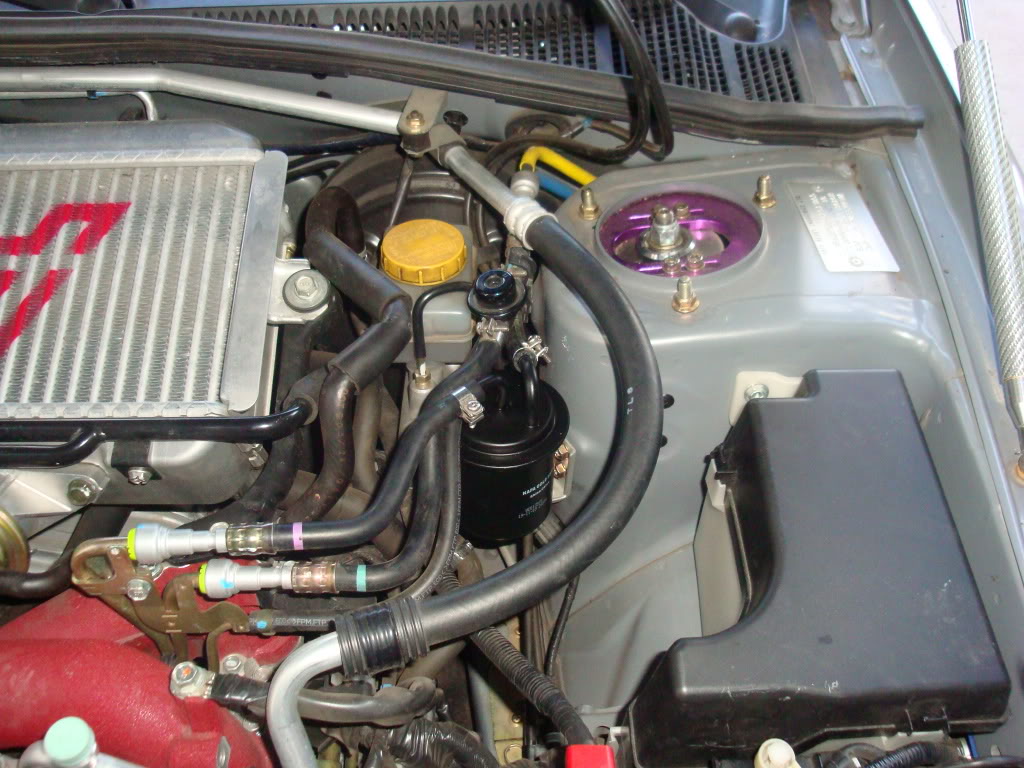
An oil cooler pipe has been added to both SVX systems. It is located in front of the radiator on the return side of the system.
Rubber Coupler
A steering shaft rubber coupler is used by both SVX systems to reduce road noise and vibration.
SVX Power Steering Pressure Switch
A power steering pressure switch is located on the outlet side of the pump. The switch monitors increased engine load during idle speed steering. The switch provides an input to the MPFI ECU, which prevents stalling by raising the engine idle speed. There is not an additional trouble code for the MPFI ECU.